Chronic venous issues affect millions of people, causing discomfort and impacting quality of life. Varithena is a modern approach to treating these conditions through minimally invasive procedures. Here is more information on this treatment, how it works, what the procedure involves, and how it helps with chronic venous issues:
What Is Varithena?
Varithena is a prescription medicine containing polidocanol in injectable foam form. The FDA has approved this treatment specifically for chronic venous insufficiency and varicose veins. The medication works as a sclerosing agent, which means it causes the targeted vein walls to collapse and seal shut.
Foam formulation allows for better contact with vein walls compared to liquid alternatives. This enhanced contact improves treatment effectiveness while reducing the amount of medication needed. Medical professionals may administer Varithena through a catheter or direct injection, depending on the specific treatment plan.
How Does It Work?
Varithena functions by damaging the inner lining of blood vessels. Once injected, the foam displaces blood within the treated vein and makes direct contact with the vessel walls. This contact triggers inflammation and eventual closure of the problematic vein.
The body naturally redirects blood flow to healthier veins after the treated vessel closes. This process typically occurs over several weeks following treatment. The closed vein eventually gets absorbed by surrounding tissue, eliminating the source of venous problems.
What Does the Procedure Entail?
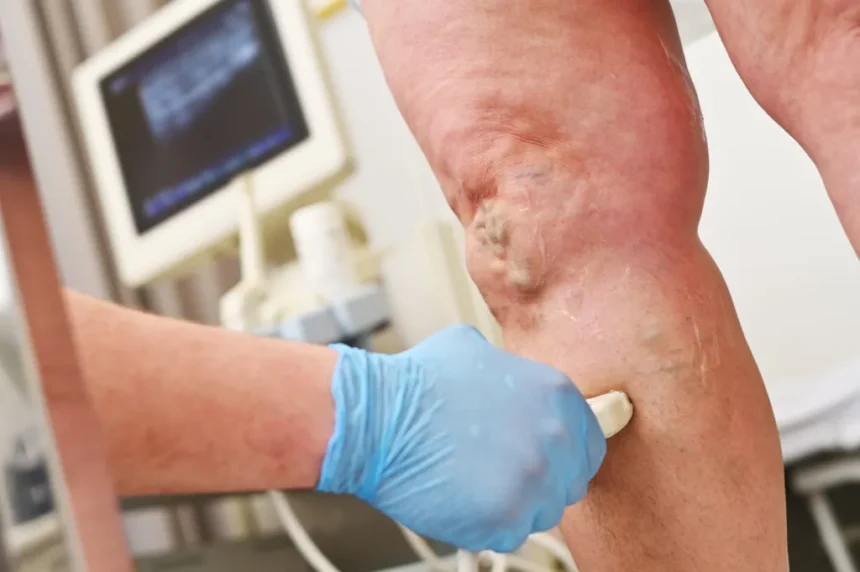
During the procedure, your healthcare provider will use ultrasound guidance to locate the affected veins and determine injection sites. Local anesthesia numbs the treatment area before the procedure begins. A small catheter or needle is inserted into the targeted vein under ultrasound guidance. The physician then injects the Varithena foam directly into the problematic vessel.
Following treatment, you may need to wear compression stockings for a specified period of time. Patients can typically return to normal activities shortly after the procedure. Your doctor may schedule follow-up appointments to monitor your healing progress and assess the effectiveness of your treatment.
What Are Chronic Venous Issues?
Chronic venous insufficiency occurs when the veins are unable to return blood from the legs to the heart effectively. This condition develops when the walls of the veins weaken or the valves become damaged, allowing blood to pool in the lower extremities. Common symptoms include leg swelling, pain, cramping, and changes to the skin.
Varicose veins represent another common venous problem characterized by enlarged, twisted veins visible beneath the skin. These veins often appear blue or purple and may cause aching, burning, or throbbing sensations. Risk factors include age, genetics, pregnancy, prolonged standing, and obesity.
How Can Varithena Help?
Varithena treatment addresses the root cause of venous problems by eliminating malfunctioning veins. Patients may experience a more subtle appearance of visible veins, as well as reduced pain and swelling. The minimally invasive nature of this treatment offers advantages over traditional surgical approaches. Recovery time is typically shorter, and the risk of complications remains low.
Treatment effectiveness varies based on individual factors. This includes vein size, location, and overall health status. Your healthcare provider will assess your specific condition to determine if this treatment option is suitable for you.
Improve Your Vascular Health Now
Varithena offers a proven solution for chronic venous insufficiency and varicose veins. This FDA-approved treatment provides effective results through a minimally invasive approach. If you experience symptoms of chronic venous issues, consult with a qualified healthcare provider to discuss treatment options. A thorough evaluation can help determine whether Varithena is suitable for your specific condition and medical history.